azure-az104-flashcards
Networking
Configure and manage virtual networking
CIDR Notation
10.0.0.0/24
10.0.0.0/16
- 192.0.2.0 -> reserved for network id
- 192.0.2.255 -> reserved for broadcast id
| IP | Subnet Mask | CCIDR |
|---|---|---|
| 192.0.2.0 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.0.2.0/24 |
| 192.0.2.0 | 255.255.0.0 | 192.0.2.0/16 |
Public IP address
- Static IP
- Dynamic IP
SKU
- Standard (static IP)
- Basic
Basic SKU: If you are creating a public IP address in a region that supports availability zones, the Availability zone setting is set to None by default. Basic Public IPs do not support Availability zones. Standard SKU: A Standard SKU public IP can be associated to a virtual machine or a load balancer front end.
Network Interface
A network interface enables an Azure Virtual Machine to communicate with internet, Azure, and on-premises resources. A virtual machine created with the Azure portal, has one network interface with default settings.
- A VM must have at least one network interface attached to it.
- Region of the NI should be the same as the VM.
- A VM can only have as many network interfaces attached to it as the VM size supports.
- NI can be applied to VM or subnet (verify)
- Stop the VM before to add a new NI.
You can only assign a network interface to a virtual network that exists in the same subscription and location as the network interface.
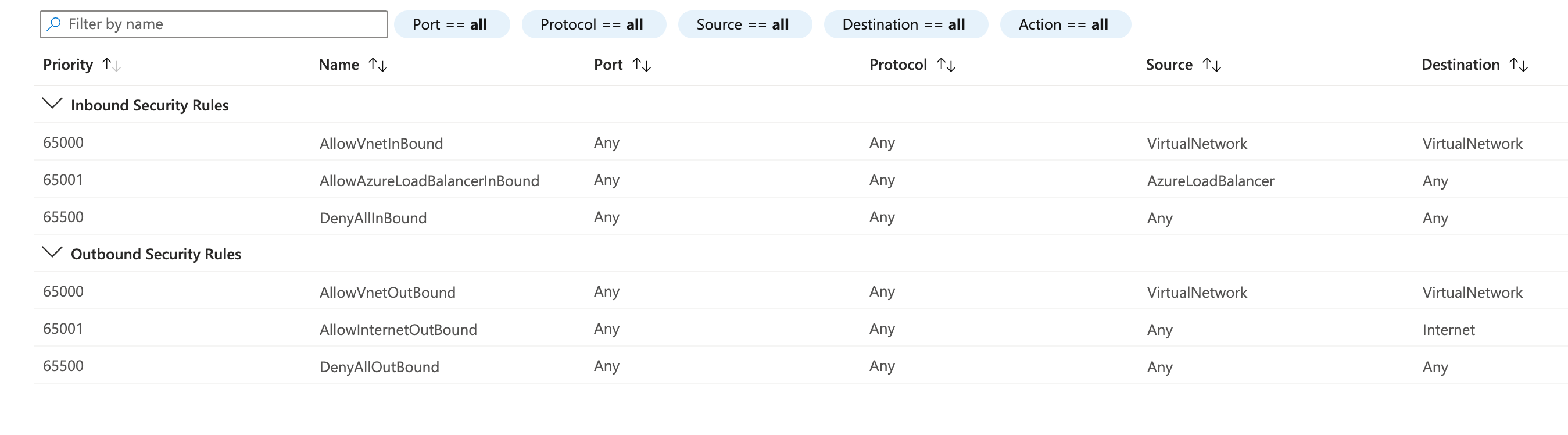
Network Security Group - NSG
You can use an Azure network security group to filter network traffic between Azure resources in an Azure virtual network. A network security group contains security rules that allow or deny inbound network traffic to, or outbound network traffic from, several types of Azure resources. For each rule, you can specify source and destination, port, and protocol.
- Inbound rules
- Outbound rules
NSG can be attached to:
| Resource | Can be attached |
|---|---|
| Network interface | :white_check_mark: |
| Subnet | :white_check_mark: |
| Virtual Network | :x: |
You can create a VM without NSG associated but it’s risky.

Default NSG
Nothing possible from external :bangbang:
Load Balancer
SKU
| Feature | Basic | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free | Charged per hour |
| SLA | NO SLA | 99,99% |
| Health Probes | TCP, HTTP | TCP, HTTP, HTTPS |
| Availability Zones Support | :x: | :white_check_mark: |
| Backend Pool | only if part of Availability Set or Availability Zones |
Also indipendent VM can be added |
| Public IP | Basic/Standard SKU | Only Standard SKU can be added |
| Public IP of the VMs | Only Public IP with basic SKU | TBV |
LB Settings
- Public IP Frontend
- Backend pool
- Health Probe
- Load Balancing Rules
Load Balancer Type
- Internal
- Public
Inbound NAT rules
NAT - Network Address Tranlation Connecting to the VM1 (without public IP) by using the NAT on the IP FrontEnd of the Load Balancer.
Example: 68.219.200.220:49152 (RDP)
- 68.219.200.220: public IP of the IP FE LB
- 49152 ephimeral port mapped internally to RDP 3389 of the internal VM
Virtual Network Peering
-
Virtual Network Peering is used to connect two Azure virtual networks together via the backbone network.
-
Azure supports connecting two virtual networks located in the same region or networks located across regions.
-
Once you enable virtual network peering between two virtual networks, the virtual machines can then communicate via their private IP addresses across the peering connection.
-
You can also peer virtual networks that are located across different subscriptions.
-
The virtual networks can’t have overlapping CIDR blocks.
Point-to-Site VPN Connection
A Point-to-Site (P2S) VPN gateway connection lets you create a secure connection to your virtual network from an individual client computer. A P2S connection is established by starting it from the client computer.
Secure connection between the on premises pc and the VM on its private IP.
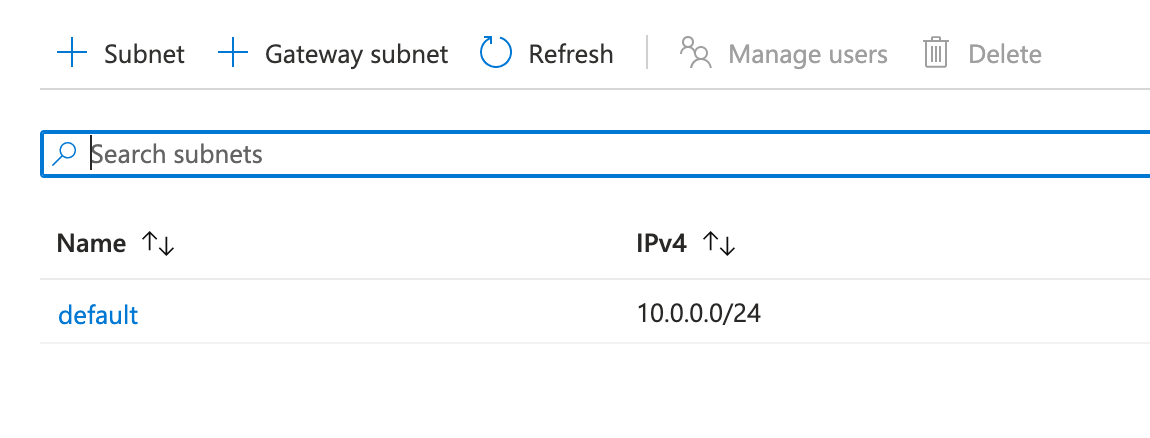
Gateway subnet
On the VN I have to install a Gateway SUbnet.
- VM
- Virtual Network
- Subnets
- (+) Gateway Subnet (can only have one GS for virtual network)
The gateway subnet is part of the virtual network IP address range that you specify when configuring your virtual network. It contains the IP addresses that the virtual network gateway resources and services use.
When you create the gateway subnet, you specify the number of IP addresses that the subnet contains. The number of IP addresses needed depends on the VPN gateway configuration that you want to create. Some configurations require more IP addresses than others. We recommend that you create a gateway subnet that uses a /27 or /28 (or /29.)
Virtual Network Gateway
- Create virtual network gateway
- link the VNG to the Gateway Subnet
- create a public IP
- VNG has a price per hour, variable depending on the Sku, no matter the usage.
Certificates
Certificates are needed for authentication to avoid any pc pc in the world can connec to the VNG.
- New-SelfSignedCertificate (CN=VPNRoot) on the server machine
- New-SelfSignedCertificate (CN=VPNRoVPNCert) on the client machine
- the client certificate is generated from the root certificate.
root certificate
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -Type Custom -KeySpec Signature `
-Subject "CN=VPNRoot" -KeyExportPolicy Exportable `
-HashAlgorithm sha256 -KeyLength 2048 `
-CertStoreLocation "Cert:\CurrentUser\My" -KeyUsageProperty Sign -KeyUsage CertSign
client certificate
New-SelfSignedCertificate -Type Custom -DnsName P2SChildCert -KeySpec Signature `
-Subject "CN=VPNCert" -KeyExportPolicy Exportable `
-HashAlgorithm sha256 -KeyLength 2048 `
-CertStoreLocation "Cert:\CurrentUser\My" `
-Signer $cert -TextExtension @("2.5.29.37={text}1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2")
Export the certificate
- Manage user certificates
- root certiticate
- export (.CER)
- save in a file
Virtual Network Gateway Configuration
- Point-to-site configuration
- Address pool: 172.16.0.0/16
-
Authentication Type: Azure
- tunnel type (IKEv2)
- link the root certificate before created (public)-> copy the content of the file before exported
- any client which needs to have the PointToSite VPN connection needs to have the client certificate installed.
Configuring the client
- install the (before generated) client certificate
- download and install the vpn client from the azure virtual Network Gateway before configured (link).
- start the vpn client and connect
Resources
Azure Point-to-Site VPN with Certificate Based Authentication
Site-to-Site VPN Connection
Azure VPN gateways provide cross-premises connectivity between customer premises and Azure.
Site-to-site VPN gateway connection from your on-premises network to the VNet.
To modify the gateway IP address for a local network gateway
If the VPN device that you want to connect to has changed its public IP address, you need to modify the local network gateway to reflect that change. :bangbang:
VNet to VNet
Connecting a virtual network to another virtual network using the VNet-to-VNet connection type is similar to creating a Site-to-Site IPsec connection to an on-premises location. Both connectivity types use a VPN gateway to provide a secure tunnel using IPsec/IKE, and both function the same way when communicating.
Azure Virtual WAN
- Create Virtual WAN from marketplace
- WM/Create Virtual Hub
- Create the VPN sites
- Connect the VPN sites to the Virtual Hub
User Defined Routes
- Scenario: CentralVM, subnet A(vmA), subnet B(vmB).
- Route Tables
- VM/Network Interface/Effective Routes
- Central VM / IP forward enabled
- On Central VM enabling forward at OS level
- now from vmA I can reach VMB through central VM